EDX
ROLLING MILL (Steel Industry)
Operational Demands of Steel Industry
Power Transmission Core
Bearings drive rolls that compress, shape, and reduce metal thickness at high speed and load.
Operate Under Stress
Thermal shock, water contamination, and massive radial loads are routine in rolling stands.
Friction & Alignment Control
Properly aligned bearings prevent roll deflection, vibration, and edge cracking of the steel.
Bearings Define Efficiency
The right bearing ensures tight tolerances, smooth finish, and continuous mill operation.

Rolling mills are used to shape metal into various forms and dimensions. Bearings in rolling mills play a vital role in supporting the high radial and axial loads generated during the rolling process. They also ensure proper alignment and smooth operation of the rolls under heavy-duty conditions.
The Edx Advantages
High Radial Load Handling
Manages force in rolling stands and work rolls.
Withstands Water & Heat
Performs under coolant spray and thermal shock.
Split Designs Available
For faster changeover without dismantling equipment.
Low Runout Tolerance
Supports dimensional accuracy in final metal output.
Bearings integrated into Rolling Mill (Steel Industry):
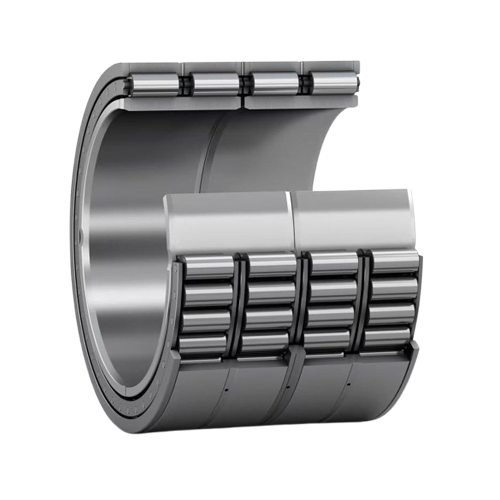
Four-Row Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Handle heavy radial loads in rolls
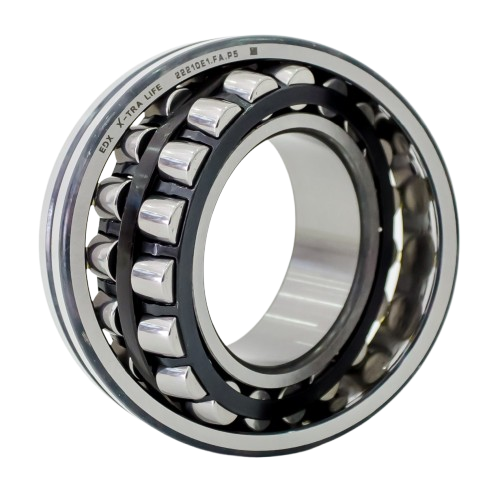
Spherical Roller Bearings
Tolerate misalignment during hot rolling
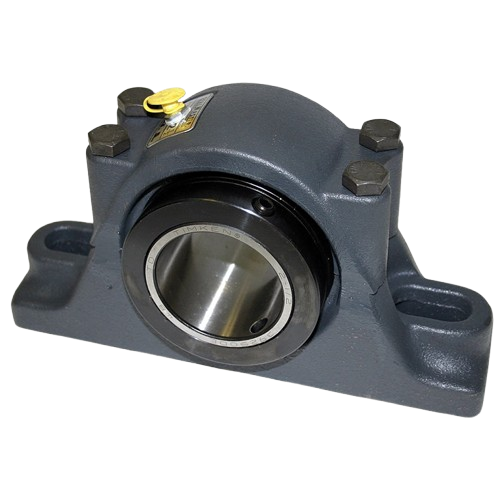
Split Bearings
Allow quick replacement without dismantling shafts
Standard Bearings vs. EDX Bearings Comparison Table
This table compares standard and EDX bearings in terms of performance features for rotating motor shafts.